In the real world, we need to prove our identity to obtain various rights and services. In the digital world, we also need an effective identity authentication mechanism to protect personal information and the security of digital assets. The fragmented nature of digital identity in the Web2 era poses a problem. Although there are login schemes associated with companies like Google or WeChat that can aggregate identity information to some extent, the problem of centralization arises. Once WeChat is blocked, the social relationships strongly tied to digital identity will also be shattered. The emergence of Decentralized Identity (DID) provides a new approach to solving these problems. DID is a decentralized identity authentication mechanism that allows each person to have a unique digital identity and control ownership of their own data. The application of DID can not only help us better manage and protect digital identities, but also provide infrastructure for data sharing, identity verification, and other scenarios. From the projects participating in the Web3 Hackathon and the topics discussed at ETHDenver, we can see the increasing popularity of the DID track. Behind this trend, there is an urgent need for privacy and security of digital identity, as well as the widespread application and promotion of decentralized technology.
The Foundation of Building a Trusted Digital World#
DID is a globally unique identifier that enables entities to be identified in a verifiable, persistent, and decentralized manner. DID enables a new distributed digital identity model that is decentralized. The advantage of DID lies in its decentralized nature. It does not rely on any single third-party identity verification institution, but achieves decentralized identity verification and management through technologies such as blockchain. This enables DID to better protect user privacy and security.
In Web3, we can complete all interactions using wallet addresses, but why do we still need DID? Because wallet addresses are not easy to remember and identify, they cannot form an impression of a person. At the same time, due to the low cost of creation, users do not cherish wallet addresses, which prevents the formation of stable identities, leading to a series of problems:
- In DAO governance, the inability to confirm address identity can lead to witch attacks.
- In DeFi, the inability to identify user identity leads to the inability to measure credit levels, resulting in higher collateral ratios and lower capital utilization.
- In Web3 social interactions, stable identity is the foundation for shaping and accumulating reputation.
Therefore, building a stable and trusted digital identity is a key focus of Web3 development, and this is also the historical mission of DID. DID is not just a name, it represents the collective behavior of the digital world. Based on the immutability of on-chain data, DID can outline a trusted digital identity, quickly gain trust, supervise collaborative behavior, and form a more trustworthy digital world.
Soul Containers and Soul Fragments#
When talking about DID, we cannot ignore another concept: SBT (Soul Binding Token). The fundamental difference between SBT and other non-fungible tokens is that SBT is non-transferable. Taking "World of Warcraft" as an example, our account is the DID, the items on the auction house are NFTs, and the bound equipment and achievements we obtain are SBTs, representing the value of our account, such as owning legendary equipment or being the first to clear a server. In the Web3 world, SBTs can record our social behavior in the digital world, and through SBTs, reputation and credit can be accumulated, building a collective behavior of digital identity. SBTs are non-transferable, like fragments of souls, infused into the container of DID, continuously enriching and perfecting the image of a digital person.
The DID system integrated with SBT can effectively solve some problems in Web3:
- In DAO governance, SBT can reduce the risk of witch attacks and give higher governance voting weights.
- In unsecured loans, SBT can be used as reputation collateral to guarantee loans and credit limits, and can be subsequently burned or replaced with repayment proofs.
- In social identity recognition, users can build stable digital portraits in Web3 interactions by obtaining a large number of SBTs. These digital portraits can be quantified and used for self-identification, depicting social identities in the digital world.
The emergence of SBTs makes us realize the difference between Web3 DID and traditional DID. This DID system integrated with SBTs can bring a more stable and trusted digital identity to Web3. Through SBTs representing experiences and achievements, it represents the unchangeable status and contributions of a person in Web3, continuously accumulating reputation and credit, and enjoying the dividends brought by this identity.
Beyond Reality, Enter the Digital World#
Currently, DID is still in the stage of continuous exploration, and its final form has not yet reached a consensus. In addition to various product forms, there are also multiple identity authentication methods. Identity authentication is the key process of connecting personal identity with the digital world. The current identity authentication methods can be roughly divided into on-chain and off-chain.
Off-chain Identity Authentication#
Off-chain identity verification is like an extension of real-world identity, which can be divided into two categories based on whether personal privacy information is collected.
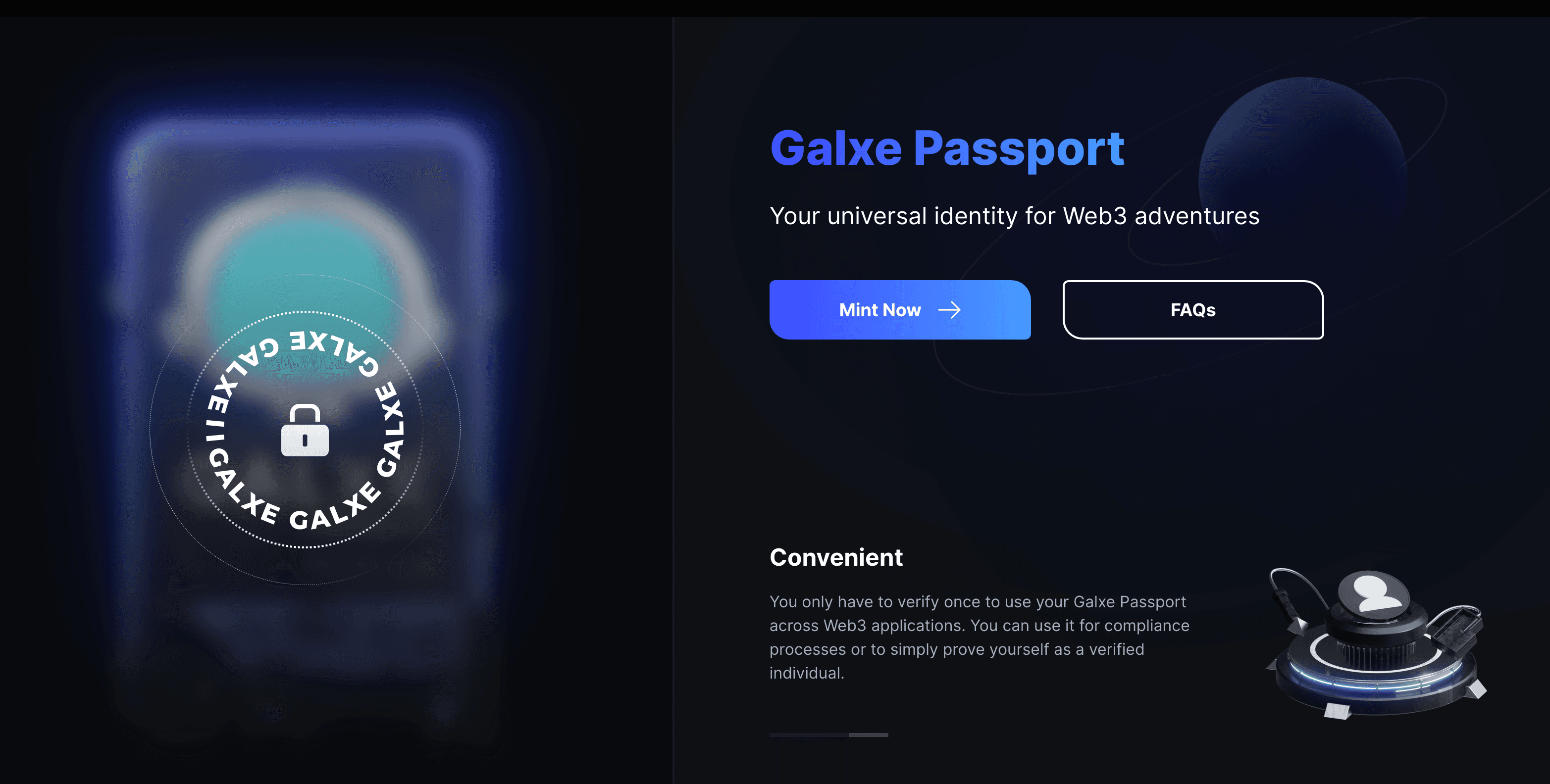
Galxe Passport is a type of DID based on SBT provided by Galxe. It requires the use of real-world proof documents such as passports, ID cards, and facial recognition information for KYC authentication. This identity authentication method can quickly surpass other competitors in terms of security and compliance. However, it has also received some criticism. In addition to concerns about privacy, this way of extending real-world identity to the digital world does not conform to the spirit of Web3.
BrightID is a decentralized anonymous social identity network that does not collect personal privacy information. Instead, it confirms the uniqueness of user identity through biometric identification. Users need to participate in verification meetings with multiple language options to complete the initial identity authentication and obtain verification badges. After establishing social connections with friends, users can obtain corresponding scores to upgrade their identity verification levels and identify false identities based on the graph formed by connections between accounts. Currently, BrightID provides a mobile app and supports connections with dozens of DApps.

Another identity authentication method is based on Web2 social platform data, such as using the social graph of WeChat to build a digital identity. This method verifies and identifies users by collecting and analyzing data on social media and constructing user relationship networks. Compared to traditional KYC methods, this method can quickly build digital identities and does not require additional personal information verification, but it also carries the risk of privacy leakage.
On-chain Identity Authentication#
On-chain identity authentication advocates abandoning real-world identity and starting anew in the digital world. It can be divided into two means: actively collecting on-chain interactions and aggregating on-chain social behaviors.
Actively collecting on-chain interactions refers to users interacting with other users on the blockchain, including transactions, holding blue-chip NFTs, holding ENS and other domain name NFTs, mainly reflecting users' financial behaviors. Through these behaviors, identity credit can be accumulated to build a digital identity. However, on the one hand, due to the relatively single data dimension and the problem of multi-chain and multi-wallet transactions, except for some whales and celebrities, ordinary users find it difficult to form a clear digital identity.
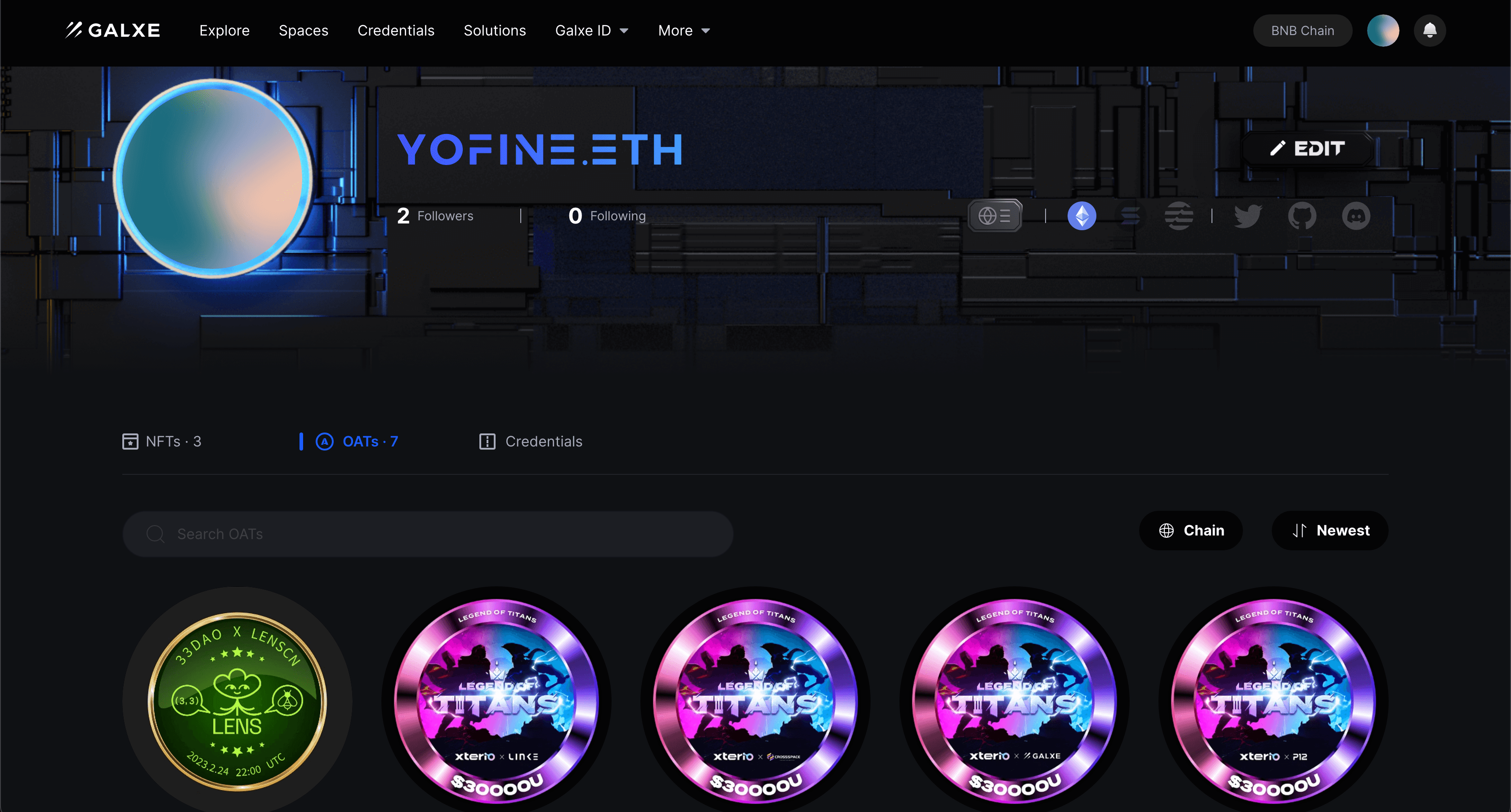
Aggregating on-chain social behaviors is an identity authentication method that aggregates and analyzes user behaviors on different social platforms, mining user social relationships in the digital world to form a user's digital identity. Usually, this authentication method quantifies user on-chain behaviors and issues an NFT as a credential after guiding users to complete a series of tasks, giving practical meaning to users' on-chain interactions and marking their personal behaviors. Representative projects of this authentication method include Layer3, Port3, Galxe, etc. Users need to complete tasks such as learning and interacting to obtain corresponding NFT credentials. These credentials not only record behaviors but can also serve as qualifications for other activities, such as lotteries. Usually, they are also connected to Web2 social platforms such as Twitter. For example, to obtain a certain NFT credential, users need to follow, like, retweet, or participate in a Space event, etc.
There are also projects that combine these two authentication methods, such as Bit islands, which include DID registration, active on-chain interaction aggregation, and support for certain social behaviors. These solutions are attempts at integration. These schemes are not black and white, but exist as a spectrum of identity types, including pure digital identities, pure real-world identities, and identities that combine the two. These identity types will be applicable to different interaction scenarios and will cooperate and coordinate as needed. Real-world identity can be an optional attribute used as a strong endorsement of credibility when communicating in the real world. Of course, these are my imaginations, and the future development still needs to be witnessed together.
Will the development of DID technology allow us to have digital souls beyond reality? Perhaps the future digital world will be filled with mysterious digital entities, each having its own unique thoughts, behaviors, and abilities. Will they be on an equal footing with humans? Or will there be an identity crisis or be controlled by identities when we have multiple identities in the digital world? Or in the future digital world, will we be able to build perfect digital replicas through DID, achieving immortality and regeneration in the digital world?
At the same time, will AI like ChatGPT also have its own unique digital identity and interact and collaborate with humans? Or with the development of DID technology, will we see more AI-based DID solutions that help us better manage and control our digital identities while protecting our privacy and data security?
Regardless of how the future digital world will be, DID technology will play a crucial role in building personal and organizational identity authentication and management in the digital world.